Lung cancer, a formidable opponent, has witnessed remarkable advancements in surgical techniques over the years. Among these, minimally invasive lung cancer surgery has emerged as a transformative approach, offering the promise of reduced recovery times, decreased postoperative pain, and shorter hospital stays. In this blog, we will explore the latest advancements in minimally invasive lung cancer surgery techniques, with a particular focus on the groundbreaking realm of robotic-assisted thoracic surgery.
Introduction to Minimally Invasive Lung Cancer Surgery
Traditional open surgery, with its inherent challenges and lengthy recovery periods, has been superseded by minimally invasive approaches. These advanced techniques, characterized by smaller incisions, specialized instruments, and cutting-edge imaging technology, strive to minimize tissue trauma. The ultimate objective is to optimize patient outcomes by facilitating faster recovery and mitigating postoperative complications.
Advent of minimally invasive techniques and their subsequent refinement has been a game-changer in the surgical management of lung cancer. The most commonly employed minimally invasive approaches for lung cancer surgery include robotic-assisted thoracic surgery, video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS), and laparoscopic surgery.
Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS)
Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS) is an innovative and minimally invasive technique that has revolutionized the field. By utilizing a thoracoscope, skilled surgeons can navigate the chest cavity through small incisions with precision. The real-time visualization on a monitor enables them to perform intricate maneuvers within the chest, resulting in numerous benefits such as reduced postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and lower infection risks. VATS has proven to be particularly effective in the treatment of early-stage lung cancer. It is truly a remarkable advancement in surgical procedures.
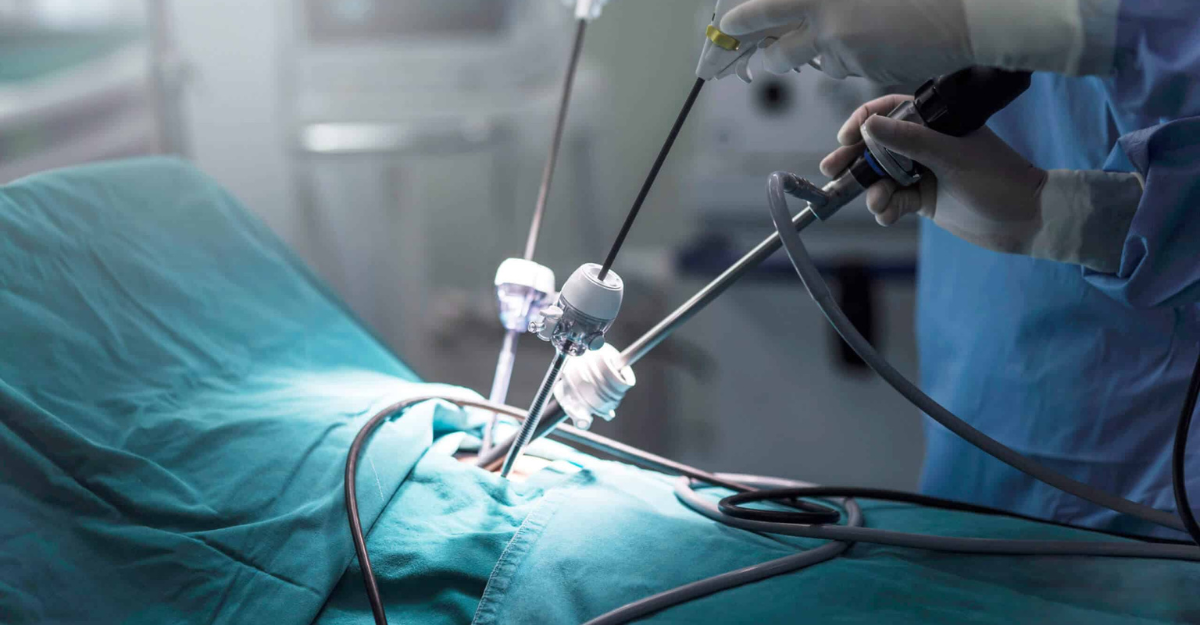
Robotic-Assisted Thoracic Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery has revolutionized thoracic procedures, ushering in an era of unparalleled precision and sophistication. This groundbreaking technique empowers surgeons to manipulate robotic arms with enhanced dexterity, providing them with a three-dimensional perspective and a broader range of motion compared to relying solely on human hands. The benefits are truly remarkable, encompassing heightened precision, minimal blood loss, reduced complication rates, and superior visualization.
a. Advanced Precision and Dexterity:
- The robotic system enables intricate maneuvers with unparalleled precision.
- Surgeons can navigate through tight spaces and execute delicate tasks with a level of control unattainable through conventional methods.
b. Reduced Blood Loss and Lower Complication Rates:
- Robotic-assisted surgery offers a minimally invasive approach, resulting in decreased blood loss during procedures.
- Enhanced patient safety and a smoother recovery process are achieved through lower complication rates.
c. Improved Visualization:
- The robotic system offers a magnified, high-definition 3D perspective of the surgical site, providing surgeons with enhanced visualization. This heightened clarity assists in the precise identification of structures, ultimately contributing to the overall success of the procedure.
d. Applicability for Complex Procedures:
- Robotic-assisted surgery is employed for complex lung cancer procedures, such as segmentectomy and mediastinal lymph node dissection.
- It offers a minimally invasive alternative for a broader range of patients, including those with challenging anatomical considerations.
Uniportal Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (U-VATS)
Uniportal Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (U-VATS) takes minimally invasive surgery to new heights. This cutting-edge approach involves performing the entire procedure through a single incision, typically measuring around 2-3 cm. With its array of benefits, including reduced postoperative pain and improved cosmetic outcomes, U-VATS is rapidly emerging as the preferred choice for various lung cancer procedures, such as lobectomy and wedge resection.
Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging
Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging revolutionizes surgical visualization by introducing a whole new dimension. Through the administration of a fluorescent dye, surgeons can effortlessly highlight structures, facilitating the precise identification of anatomical landmarks. This real-time guidance significantly mitigates the risk of harm to surrounding tissues, thereby enhancing the overall safety of the procedure. Fluorescence imaging is particularly invaluable in the identification and preservation of vital structures during lung cancer surgery.
Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy (ENB)
Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy (ENB) utilizes cutting-edge imaging and electromagnetic technology to navigate through the bronchial tree. This innovative technique allows for accurate targeting of lung lesions, facilitating biopsies and treatments. With its minimally invasive approach and enhanced precision in reaching peripheral lung lesions, ENB has become an invaluable tool for the diagnosis and staging of lung cancer.
Future Trends and Innovations
Looking ahead, the trajectory of minimally invasive lung cancer surgery is marked by several exciting trends and innovations.
a. Artificial Intelligence in Surgical Planning:
- By integrating AI for preoperative planning and intraoperative decision-making, surgeons can analyze imaging data to optimize incisions and approaches.
- This not only streamlines the surgical process but also contributes to personalized and effective treatment strategies.
b. Advancements in Instrumentation:
- Ongoing developments in specialized instruments, particularly in the realm of robotic surgery, enhance precision and maneuverability.
- As these instruments evolve, surgeons gain greater capabilities in navigating complex anatomical structures.
c. Personalized Medicine Approaches:
- Tailoring surgical approaches based on individual patient characteristics and genomic information allows for more targeted and effective treatment.
- This personalized approach ensures that the surgical plan aligns with the unique attributes of each patient and their specific lung cancer.
Conclusion
The latest advancements in minimally invasive techniques for lung cancer surgery, particularly in the realm of robotic-assisted thoracic surgery, represent a significant shift in the field of thoracic surgery. These innovations not only equip surgeons with new tools but also instill hope in patients by combining effectiveness with reduced invasiveness.
As technology continues to evolve, the future holds the promise of even more sophisticated approaches, integrating artificial intelligence and personalized medicine. The synergy of these innovations is not only changing the way surgeons approach lung cancer but also improving the overall experience for patients, with shorter recovery times and improved quality of life. The collaboration of these cutting-edge techniques is paving the way for a new era in lung cancer surgery, where precision meets compassion in the pursuit of optimal patient outcomes.